- Vidya Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- GST NO. : 23AADCL3954C1ZV
- +91-8889017888
100 piece (MOQ)
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier, Trader, Distributor |
| Brand Name | ETEILY |
| Color | Cream |
| Certification | CE Certified, ISI Certified, ISO 9001:2008 |
| Click to view more | |
Preferred Buyer From
| Location | Worldwide |
Product Details
Feature
Fast Signal Stength, Hard Structure, Heat Resistant, High Acurace, Rust Proof, Waterproof
Type
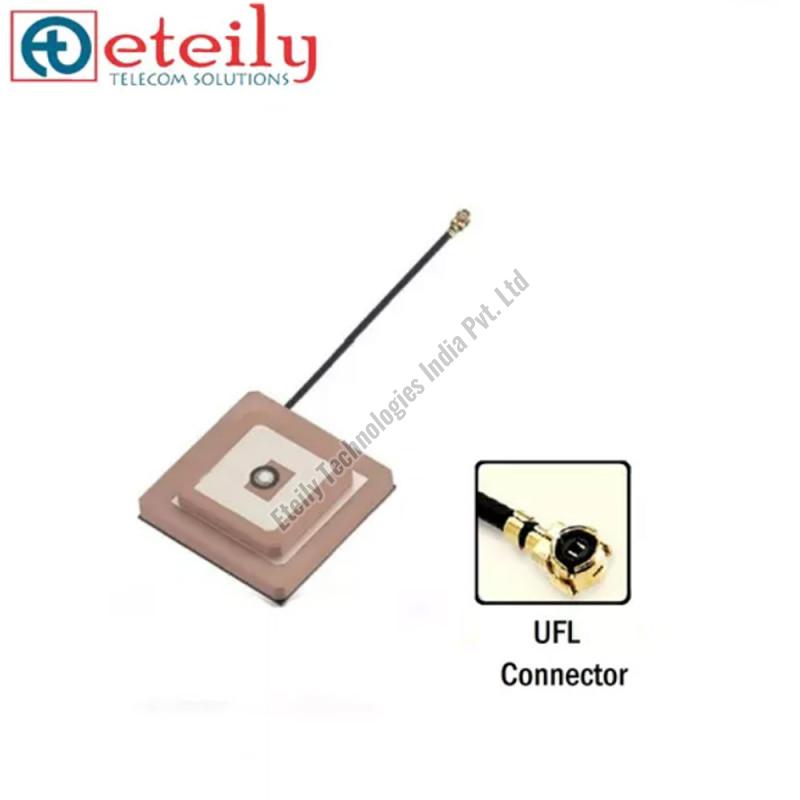
Internal Antenna
Frequency
1575.42MHz / 1227.6MHz
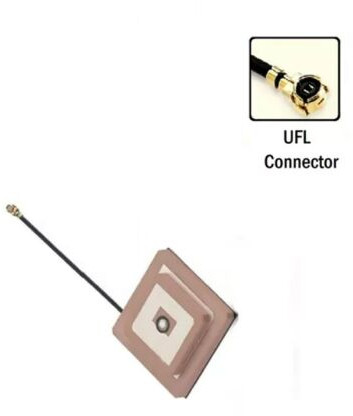
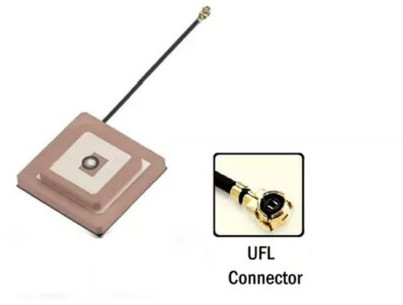
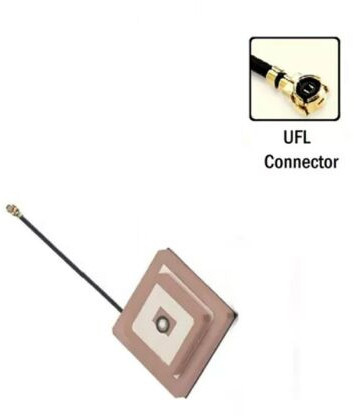
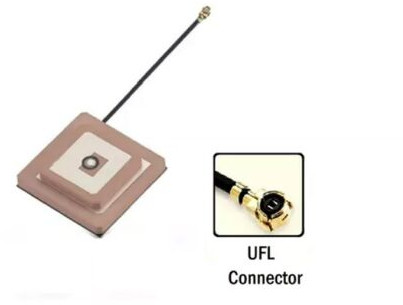
Product
Antenna
Technology
Omnidirectional
Mounting
Thru-Hole Mount Ceramic
Dimension
Top Layer:18x18mm; Bottom Layer: 25x25mm
Product Code
ET-L1L2PA-5L10C25x18-U
Payment Terms
L/C, D/A, D/P, T/T, Western Union
Delivery Time
5 Days
An embedded active dual-band GNSS L1/L2 GPS internal PCB antenna is designed for applications where space is limited, and you need an antenna that can be integrated directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB). Here's a detailed overview of this type of antenna:
Key Features and Specifications-
Frequency Bands:
- L1 Band: Operates around 1.575 GHz, commonly used for GPS signals.
- L2 Band: Operates around 1.227 GHz, also used for GPS signals and often for military or high-precision applications.
-
Active Antenna:
- Built-in Amplifier: An active antenna includes an internal amplifier to boost the received signal. This can improve performance, especially in environments with weak signals or interference.
-
Embedded Design:
- Internal PCB Mount: Designed to be mounted directly onto a PCB, which is ideal for compact devices and applications where external antennas are impractical.
-
Dual-Band Capability:
- L1/L2 Support: The antenna is capable of receiving signals on both the L1 and L2 bands, allowing for better accuracy and robustness in GNSS applications.
-
Connector:
- Direct Connection: Usually, the antenna connects directly to the PCB without the need for external connectors. Ensure that the antenna's design is compatible with your PCB layout.
-
Size and Form Factor:
- Compact: These antennas are typically small and designed to fit within the constraints of a PCB, making them suitable for portable and embedded devices.
-
Performance Specifications:
- Gain: Check the gain specification to understand how well the antenna will perform. Higher gain usually translates to better reception.
- Noise Figure: An important parameter for active antennas, indicating the level of noise introduced by the antenna's amplifier.
-
PCB Design:
- Ensure the PCB design includes the necessary footprint and solder pads for mounting the antenna.
- Consider the antenna's placement to avoid interference from other components and ensure optimal signal reception.
-
Power Supply:
- Active antennas require a power supply for the internal amplifier. Ensure your design includes the necessary power connections and check the voltage and current requirements.
-
Signal Integrity:
- Use high-quality PCB materials and ensure proper impedance matching to maintain signal integrity between the antenna and the GNSS receiver.
-
Testing and Calibration:
- After integration, test the antenna performance to ensure it meets your requirements. Calibration may be necessary to optimize performance in your specific application.
-
Environmental Considerations:
- Verify that the antenna is suitable for the environmental conditions of your application, including temperature and humidity.
- Embedded Systems: Ideal for use in devices where space is at a premium, such as handheld devices, wearables, or automotive systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Suitable for GPS-enabled electronics where an external antenna is not feasible.
- Industrial Equipment: Used in equipment that requires accurate positioning in a compact form factor.
Looking for "Embedded Active Dual Band GNSS L1/L2 GPS Internal PCB Antenna" ?
piece