- Vidya Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- GST NO. : 23AADCL3954C1ZV
- +91-8889017888
100 Piece (MOQ)
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier, Trader, Distributor |
| Color | Black |
| Condition | New |
| Certification | CE Certified, ISI Certified |
| Click to view more | |
Preferred Buyer From
| Location | Worldwide |
Product Details
Feature
Auto Controller, Dipped In Epoxy Resin, Durable, High Performance, Stable Performance
Type
Antenna,Internal Pcb Antenna,Internal PCB Antenna
Country of Origin
India
Technology
2g Gsm Cellular
Mounting
Surface Mount
Product
Antenna
Product Code
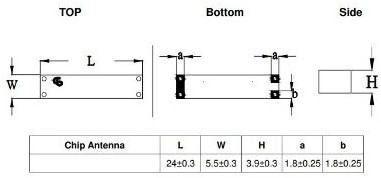
ET-WAG-P-LTE10-00-001
Payment Terms
L/C, D/A, D/P, T/T, Western Union
Delivery Time
5 Days
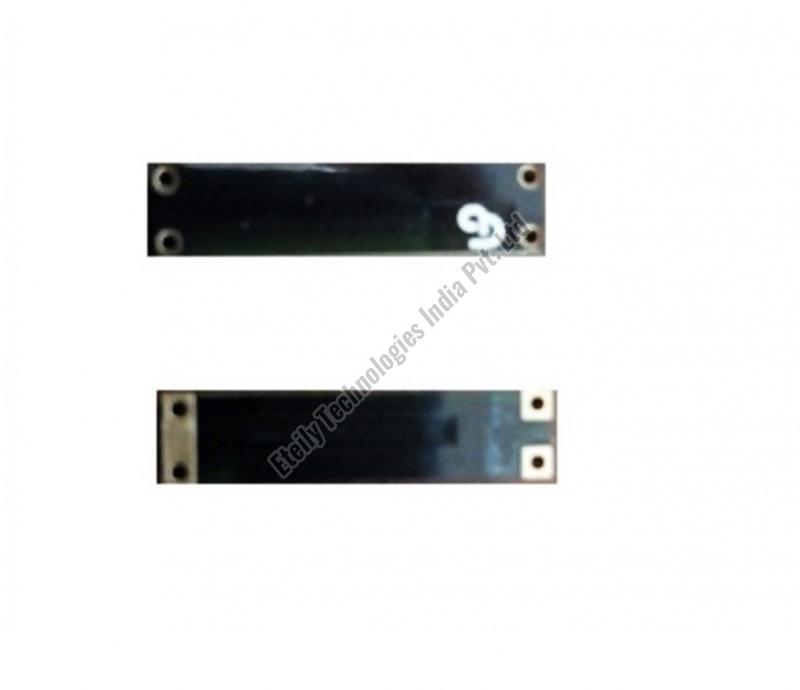
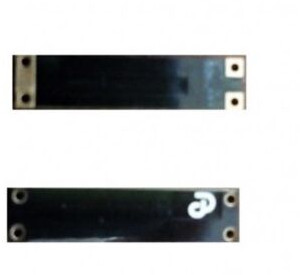
A 2G/3G/LTE surface mount antenna is designed to be mounted directly onto a circuit board (PCB) and is compatible with a range of cellular network frequencies. Here’s a breakdown of its features and typical use cases:
-
2G/3G/LTE Compatibility:
- 2G: Refers to the second generation of mobile networks, such as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications).
- 3G: Refers to the third generation of mobile networks, including technologies like UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) and HSPA (High-Speed Packet Access).
- LTE: Long-Term Evolution, also known as 4G, which provides high-speed data and improved network performance.
-
Surface Mount:
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT): This means the antenna is designed to be soldered directly onto the surface of a PCB. Surface mount antennas are preferred for their compact size and ease of integration into electronic devices.
-
Antenna Features:
- Frequency Range: The antenna is tuned to operate across the frequencies used by 2G, 3G, and LTE networks, making it versatile for various cellular applications.
- Size and Form Factor: Surface mount antennas are generally compact, designed to fit into space-constrained environments, and optimized for performance while maintaining a small footprint.
-
Use Cases:
- Embedded Systems: Ideal for devices like IoT modules, portable gadgets, or industrial equipment where space is limited, and a robust cellular connection is needed.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in devices like smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices where an internal, space-efficient antenna is required.
-
Advantages:
- Compact Design: Takes up less space compared to external antennas.
- Ease of Integration: Simple to integrate into a PCB design, often used in mass-produced electronics.
When selecting a surface mount antenna, consider factors such as the specific frequency bands your application needs, the physical space available on the PCB, and any mechanical or environmental requirements of the device.
Looking for "2G/3G/LTE Surface Mount Antenna" ?
Piece