- Vidya Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- GST NO. : 23AADCL3954C1ZV
- +91-8889017888
100 piece (MOQ)
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier, Trader, Distributor |
| Brand Name | ETEILY |
| Material | Copper |
| Color | Golden |
| Click to view more | |
Preferred Buyer From
| Location | Worldwide |
Product Details
Condition
New
Application
Electrical Adaptor
Certification
CE Certified, ISI Certified
Type
Internal Antenna,Internal Antenna
Product
Antenna
Technology
WiFi
Radiation
Omnidirectional
Frequency
2400~2500MHz
Gain
2dBi
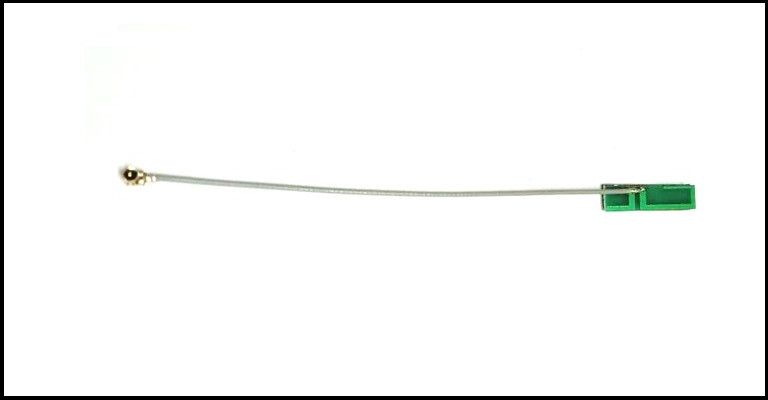
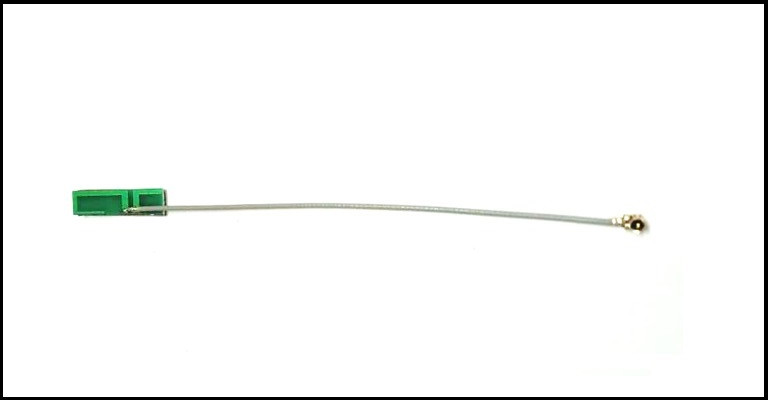
Connector
UFL Right Angled
Cable
1.13mm
Product Code
ET-WI2PC-5L10CP4-U
Payment Terms
L/C, D/A, D/P, T/T, Western Union
Delivery Time
5 Days
A 2.4GHz 2dBi internal PCB antenna is a specific type of antenna used in wireless communication, particularly for devices operating on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is common for Wi-Fi and other wireless technologies. Here's a detailed breakdown of its characteristics:
Key Features:-
2.4GHz Frequency:
- Purpose: This antenna is designed to operate at the 2.4 GHz frequency band, which is commonly used for Wi-Fi (802.11b/g/n), Bluetooth, and some other wireless communication standards.
- Band: It’s part of the ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band that is unlicensed and widely used for various wireless applications.
-
2dBi Gain:
- Gain: The 2dBi indicates the antenna's gain, which measures how much power the antenna can focus in a particular direction compared to an isotropic radiator (a theoretical antenna that radiates equally in all directions). A 2dBi gain means that the antenna provides a modest increase in signal strength over an isotropic radiator.
- Performance: A 2dBi gain is relatively low, making this type of antenna suitable for shorter-range communication or scenarios where high gain is not critical. It typically provides good coverage for small to medium-sized areas, such as within a room.
-
Internal PCB:
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Antenna: This type of antenna is integrated directly into the circuit board of a device. It’s designed to be compact and cost-effective, and is often used in devices where space is limited or where external antennas are not practical.
- Design: PCB antennas are etched onto the surface of the PCB and are generally small, making them ideal for compact electronic devices.
-
Internal:
- Mounting: As an internal antenna, it’s embedded within the device rather than mounted externally. This helps maintain a compact design and avoids the need for external protrusions.
- Integration: Internal antennas are commonly used in devices like smartphones, tablets, routers, and other compact electronics where external antennas would be cumbersome or visually unappealing.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops to provide Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity.
- IoT Devices: Ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) devices where space is limited and external antennas are not feasible.
- Wireless Modules: Found in various wireless modules and embedded systems where an internal antenna solution is preferred for its compactness and ease of integration.
-
Benefits:
- Compact Design: Internal PCB antennas save space and are ideal for small devices.
- Cost-Effective: Integrating the antenna into the PCB reduces manufacturing costs and complexity.
- Aesthetic: Eliminates the need for external antennas, contributing to a cleaner device design.
-
Limitations:
- Limited Gain: With a 2dBi gain, the antenna provides lower signal strength compared to higher-gain antennas, which may limit its effective range and performance in challenging environments.
- Placement Sensitivity: Performance can be affected by the placement of the antenna within the device and the materials surrounding it.
Looking for "2.4GHz 2dBi Internal PCB Antenna with 1.13mm (L-10CM) + UFL Connector" ?
piece